Research has confirmed the discovery of a new mineral, tantalum, at Bewadze-Mankoadze in the Kibi-Winneba Belt of southern Ghana. This mineral is present in significant quantities within an igneous rock known as pegmatite.

The findings were detailed in a published paper by Dr. Emmanuel Daanoba Sunkari, a lecturer at the University of Mines and Technology (UMat); Joshua Nkansah, a postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Johannesburg and affiliated with UMat; and Salaam Jansbaka Adams from the University of Environment and Sustainable Development.
Their study is titled “Geochemical Exploration for Tantalum in Coltan-Rich Pegmatites at Bewadze-Mankoadze Area of the Kibi-Winneba Belt, Southern Ghana: Constraints from Exploratory Data Analysis.”
The research involved petrographic studies of rock samples from pegmatite outcrops and statistical analyses of major and minor elements to identify potential tantalum deposits in the area.
The team collected ten samples from each town for whole-rock geochemistry and prepared thin sections from selected samples for further analysis.
The study found geochemical anomalies in the southwestern portion of the area through single and multi-element halo mapping, suggesting that exploration efforts for tantalum mineralization should focus on this region.
The researchers noted that pegmatites are abundant in southern Ghana, particularly in the Ewoyaa, Biriwa, Winneba, Bewadze, and Mankoadze areas.
They emphasized that this study contributes to the global transition to clean energy, as tantalum is a critical mineral used in producing capacitors, which play a vital role in energy-saving technologies, including renewable energy systems that enhance energy storage and transport in solar panels, wind turbines, and electric vehicles.
If economically harnessed, the tantalum deposit could significantly boost Ghana’s foreign exchange earnings and provide by-products for clean energy production.
The researchers also indicated that the tantalum-bearing pegmatites in the Bewadze-Mankoadze area contain various valuable minerals, such as spodumene, beryl, and tourmaline.
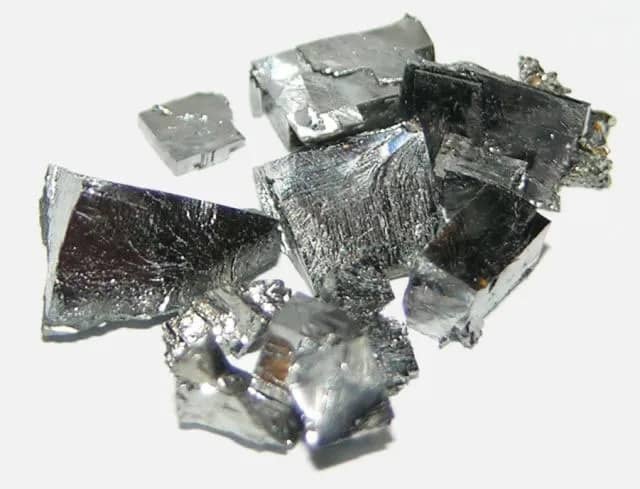
Tantalum, represented by the symbol Ta and atomic number 73 in the periodic table, derives its name from Tantalus, a figure from Greek mythology.
In its pure form, tantalum appears as a shiny, silvery metal, known for its corrosion resistance and stability at high temperatures.
This mineral is primarily used in manufacturing electronic components and high-temperature devices, including aircraft engines.
Additionally, it serves as an alloying agent to harden metals and is widely utilized in capacitors, as well as in various medical and dental applications.





















































![[FREE FREE MONEY] Predict and Win a Guaranteed GH¢200 From Us EVERY WEEK](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/02/Predict-and-Win-Final-09-03-2021-218x150.jpg)
![[Predict & Win – 8th/Oct.] WIN A Guaranteed ¢200 From Us This Week](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/maxresdefault-16-218x150.jpg)
![[Predict & Win – 2nd] WIN A Guaranteed ¢200 From Us This Week](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/maxresdefault-50-218x150.jpg)
![[Predict & Win – 25th] WIN A Guaranteed ¢200 From Us This Week](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/maxresdefault-36-218x150.jpg)
![[Predict & Win – 18th] WIN A Guaranteed ¢200 From Us This Week](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/09/maxresdefault-23-218x150.jpg)










![[National cathedral] See full list of churches that have contributed since 2018](https://wordpress.ghanatalksradio.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/09/Ghana-National-Cathedral-GhanaTalksRadio-100x70.jpg)



